In this lab, you’ll be writing a generic array-filtering function. This will make use of pointer arithmetic, function pointers, and pointer casting. This is an actually useful function! Filtering values out of an array is a very common operation.
Starting off
wgetthese materials on thoth- unzip
- rename
abc123_lab6.cwith your username - edit
compile.shto replaceabc123with your username chmod +x compile.sh./compile.shto ensure it compiles properly./lab6should show:
there are 0 floats less than 50:
there are 0 floats that have an even whole part:
there are 0 bytes less than 50:
You will do your work in the _lab6.c file just like on lab 4.
Predicates
“Predicate” is a common programming term which means “something that gives a yes-or-no answer.”
The filter function’s predicate must be a function which:
- takes a
const void*which points to a value from the array - returns a
bool:- false to ignore the item, and
- true to put the item in the output array
This is typedef‘ed for you in lab6.h as:
typedef bool (*PREDICATE)(const void*);
So that’s what PREDICATE means in filter’s arguments.
1. Writing the predicate functions
The less_than_50 function should interpret its parameter as a pointer to a float, and as the name implies, return true if it is less than 50. Don’t forget to remove the (void)p; line in this and the other predicates as you write them.
Since the parameter is a const void*, you’ll have to cast the parameter to a different pointer type.
Have a look at how I wrote the compare_ints function in the qsort.c example to get an idea of how to write this. Important: note that you have to cast the pointer to a different pointer type, then dereference the pointer to get the actual value.
Then implement the others:
even_whole_numbershould interpret its parameter as a pointer to afloat, and returntrueif the whole number part of the float is even.- you can cast a
floatto anintto get the whole number part. (This doesn’t mean casting afloat*to anint*. That’s a totally different operation.)
- you can cast a
less_than_50_bshould interpret its parameter as a pointer to achar, and returntrueif the value is less than 50.
Hint: comparison operators give you a truth value that can be used anywhere a bool is execpted. You can write e.g. return x == 10;. This is valid in C and Java.
2. Writing the filter function
Have a look at the first piece of code in lab6_tester.c’s main:
float filtered[NUM_VALUES];
int filtered_len = filter(filtered, float_values, NUM_VALUES, sizeof(float), &less_than_50_f);
printf("there are %d floats less than 50:\n", filtered_len);
for(int i = 0; i < filtered_len; i++)
printf("\t%.2f\n", filtered[i]);
Look at the float_values array and think about what the output should look like. (There are 6 numbers less than 50, right?)
In _lab6.c, your filter function should work like this:
- for each item in the
inputarray:- call the
predfunction with a pointer to that element- it’s a function pointer but you just call it like a function
- like
if(pred(whatever))
- if it returned “true”:
- use
memcpyto copy that item from the input array to the output array (see below)
- use
- call the
In addition it should:
- keep a count of how many items “passed the test” (predicate returned “true”)
- return that count
memcpy
memcpy is used to copy blobs of bytes from one place to another. It’s very widely used.
memcpy(dest, src, length);
This will copy length bytes from the memory pointed to by src into the memory pointed to by dest. It’s also a generic function, as it doesn’t care what the bytes mean, it just copies them.
“Walking pointers”
You’re used to using [] to access values from arrays. But you can’t use [] on a void*. Instead, another technique is to use a “walking pointer.”
Instead of keeping a pointer to the beginning of an array, we move the pointer along, item by item, to access the array. Like this.
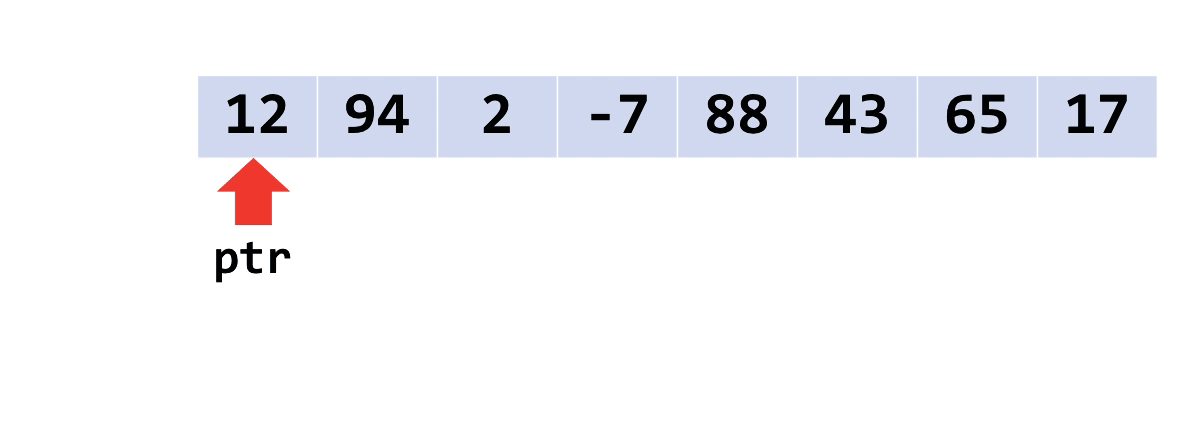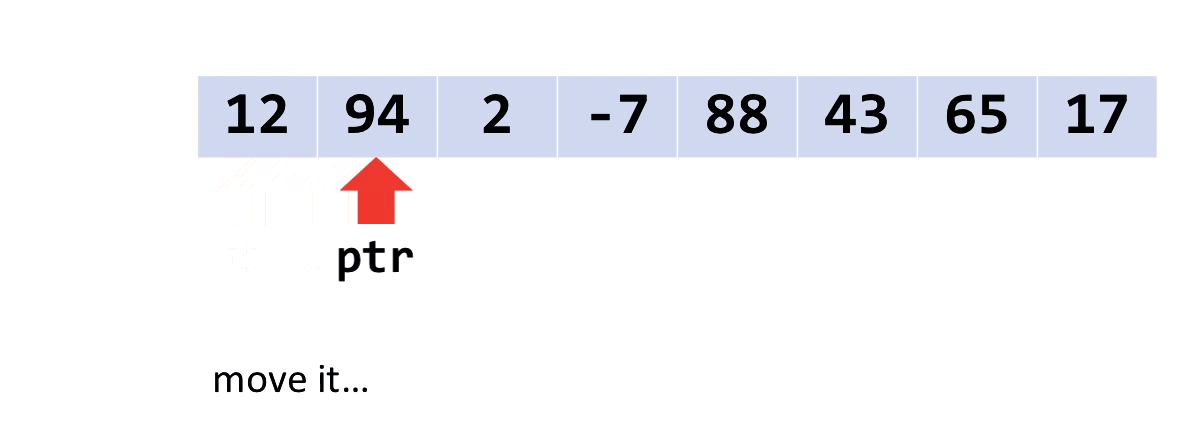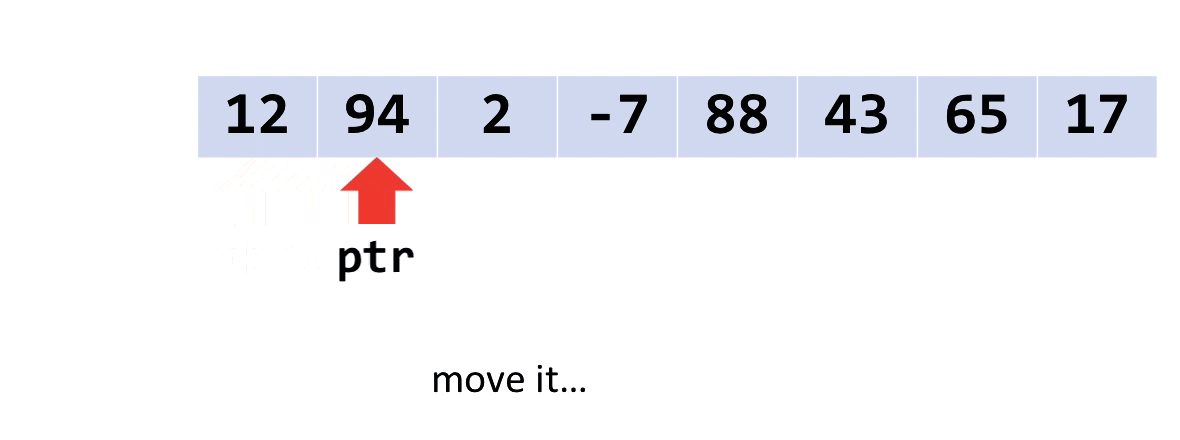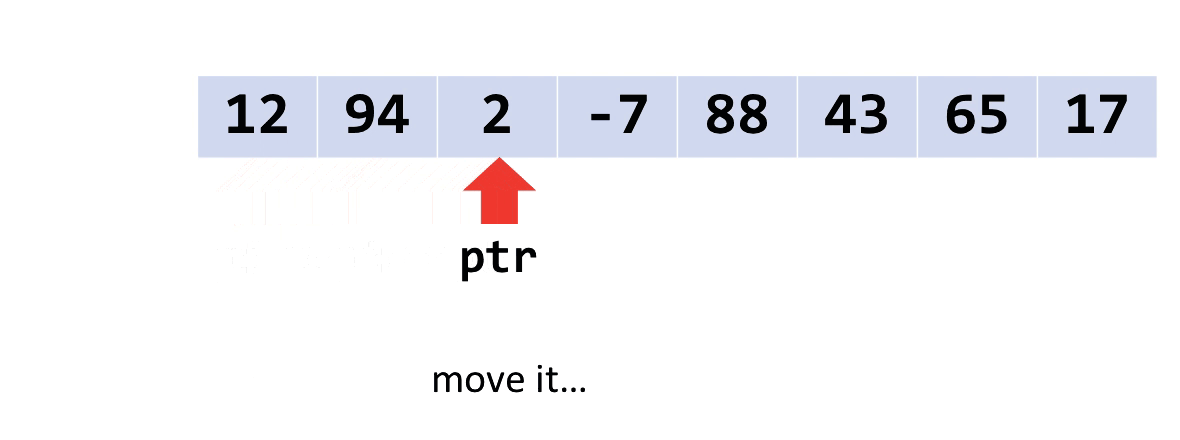
When you do pointer arithmetic on a void*, it will add or subtract a number of bytes to its address. So, you can move the pointer(s) along by adding the size of one item to them.
I think technically this behavior is a nonstandard gcc extension and that in standard C you cannot perform pointer arithmetic on a
void*, but whatever I don’t care. you’d just be casting to and from achar*in standard C. whatever
The correct output
Done right, the output should be:
there are 6 floats less than 50:
31.94
36.10
1.00
6.35
20.76
19.60
there are 3 floats that have an even whole part:
36.10
6.35
20.76
there are 6 bytes less than 50:
31
36
1
6
20
19
Some likely mistakes:
If you don’t move the pointer along the input array, you’ll get something like:
there are 10 floats less than 50:
31.94
31.94
31.94
...etc...
If you don’t move the pointers by the right number of bytes, you might get something like:
there are 6 floats less than 50:
127.76
36.10
0.00
...etc...
If you moved the input pointer right, but forgot to move the output pointer along:
there are 6 floats less than 50:
19.60
0.00
0.00
...etc...
If you moved BOTH pointers every iteration:
there are 6 floats less than 50:
31.94
0.00
36.10
...etc...
If you didn’t count properly, or maybe you didn’t respond to the predicate properly:
there are 0 floats less than 50:
Submission
You’ll submit your _lab6.c to gradescope as usual. Note that the autograder will put your filter function through a more thorough test using different arrays and predicates than the ones I’ve given you to make sure it really is generic.